In the ever-evolving realm of wireless technology, WiFi 7 emerges as the next generation standard poised to redefine the benchmarks for connectivity. This detailed exploration delves into the intricacies of WiFi 7, covering its key features, technological advancements, and potential implications for the future of wireless communication.
- Standardization: Wi-Fi 7 corresponds to IEEE 802.11be (EHT standard: Extremely High Throughput). IEEE 802.11be is in the early stages of development, with the official release of the IEEE 802.11be standard expected in the first half of 2024. Organizations such as the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the WiFi Alliance are working on standardization.
- Frequency Bands: While specific frequency bands are yet to be finalized, WiFi 7 is expected to explore higher frequency ranges, potentially including the 6 GHz band.
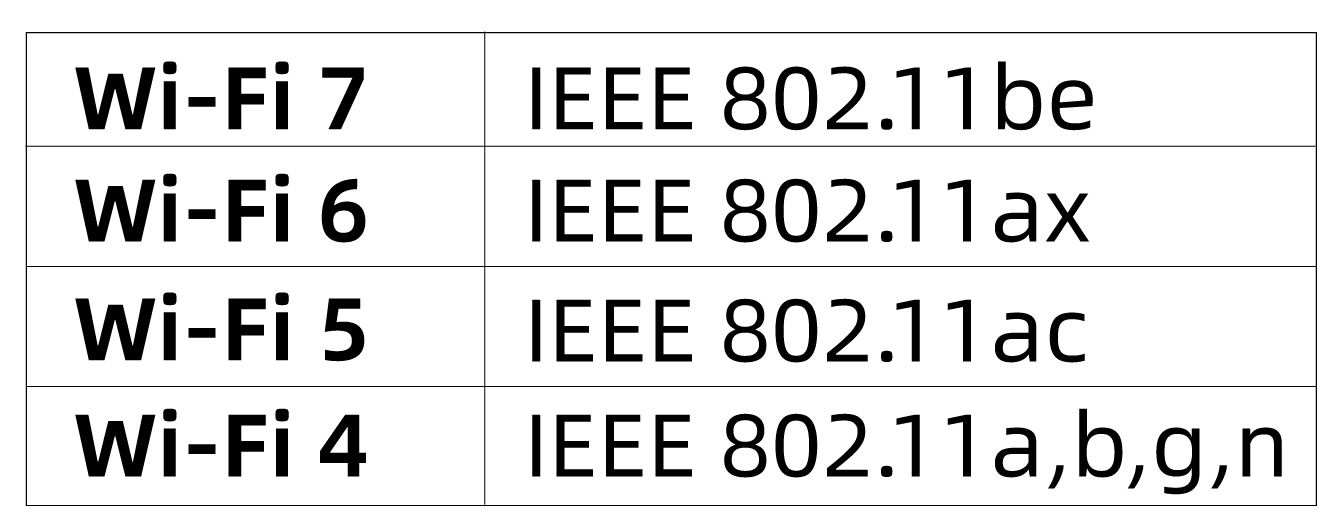
- Wi-Fi follows the IEEE 802.11 standard.The Wi-Fi Alliance uses simplified generational names for Wi-Fi. The technical standards (supporting technologies) corresponding to Wi-Fi 4 through Wi-Fi 7 are listed below:
- Multi-Gigabit Speeds: WiFi 7 aims to deliver multi-gigabit speeds, surpassing its predecessors. The anticipated data rates are expected to far exceed those of WiFi 6, supporting applications requiring ultra-fast connectivity.
- Advanced Modulation Techniques: WiFi 7 is likely to incorporate advanced modulation and coding schemes, optimizing spectrum efficiency and enhancing overall network performance.
- Improved Channel Management: Efforts are underway to refine channel management techniques, addressing interference issues and ensuring a more reliable wireless experience.
- Targeted Reduction: Recognizing the importance of low latency for applications like gaming and real-time communication, WiFi 7 aims to further reduce latency, providing an instantaneous and responsive user experience.
- Integration of New Technologies: Integration of technologies like Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) and Basic Service Set (BSS) Coloring contributes to minimizing latency.
- Enhanced MU-MIMO: Building upon the Multi-User, Multiple Input, Multiple Output (MU-MIMO) technology introduced in previous standards, WiFi 7 is expected to support an increased number of simultaneous connections.
- High-Density Environments: This improvement is particularly valuable in high-density environments, catering to the growing number of connected devices.
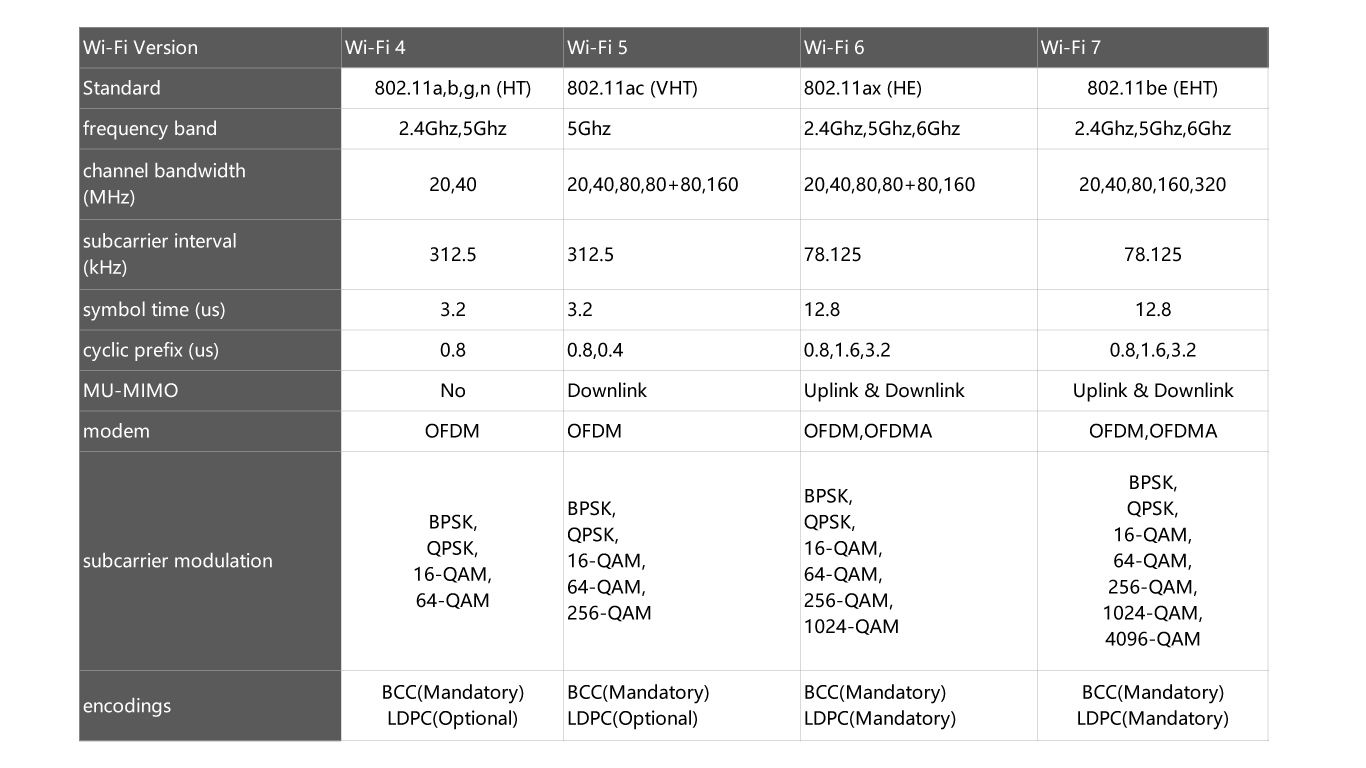
The physical layer standards from 802.11n (HT) to 802.11be (EHT) are as follows:
- Advanced Encryption Standards: WiFi 7 places a strong emphasis on security, incorporating the latest encryption standards and authentication mechanisms to address evolving cyber threats.
- Development Stage: As of now, WiFi 7 is in the development phase, with standardization efforts and technical specifications being refined.
- Commercial Deployment: The commercial deployment of WiFi 7-enabled devices is expected in the coming years, pending the completion of standardization and regulatory approvals.
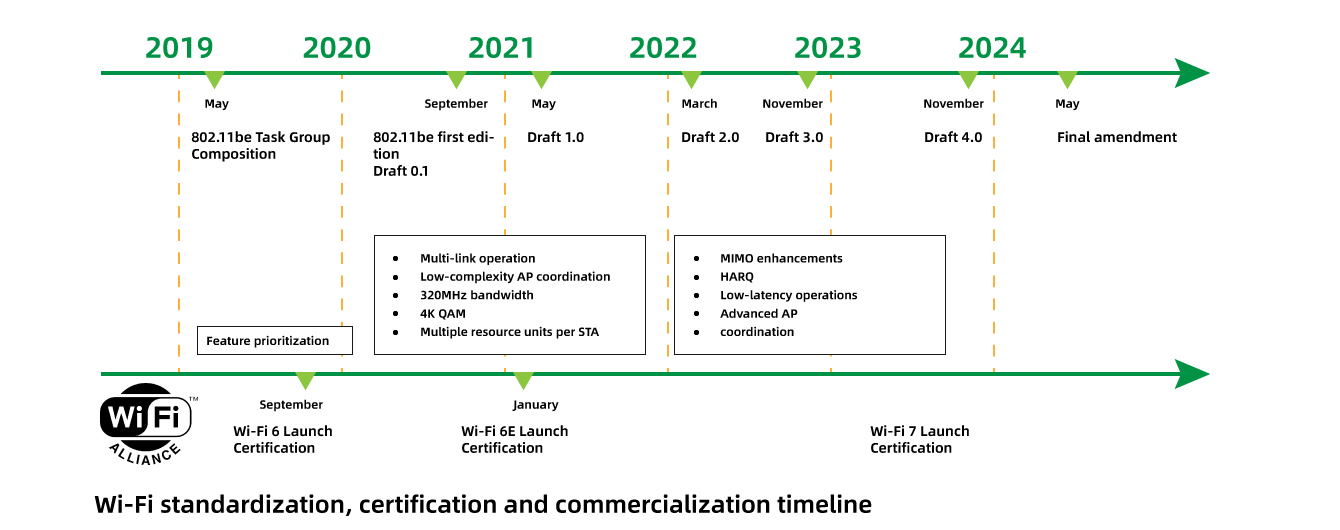
The Wi-Fi7 standardization certification and commercialization schedule is as follows:
WiFi 7 represents a leap forward in wireless connectivity, promising unparalleled data rates, enhanced spectrum efficiency, low latency, and improved security. As the standard progresses from development to adoption, it holds the potential to revolutionize how we experience and engage with wireless networks, ushering in a new era of connectivity that is faster, more reliable, and more responsive than ever before. While challenges and refinements lie ahead, WiFi 7 stands as a testament to the relentless pursuit of innovation in the pursuit of an interconnected future.